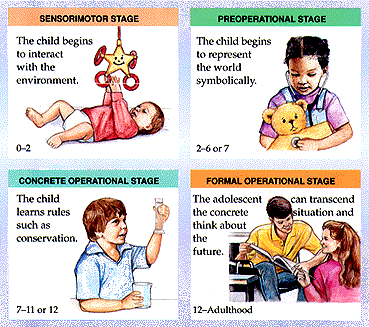
¿ What is a human development theory? Is an ordered set of principles and hypotheses that try to explain the development and that are intended to provide a theoretical framework for research.
Motor Development
The motor development involved in the same way internal and external factors. Internal factors could be the genetic material, sex or hormones and the external factors are the nutrition, the weather,the social class,etc.
to talk about the motor development we have to take into account the laws of growth and physical development. The motor development is produced by:
Cefalocaudal low: development occurs from the upper body (the head), to the bottom ( feet).
Proximodistal law : is produced from the central part towards the extremes of the body. The child controls before the movements of the arms than the hands,and the movement of the hands prior to the fingers.
Flexors and extensors law: The flexors are the muscles that flex the joints and the extensors are the muscles that provoque the aperture of the joints. The child lean first to pick up an object than drop out the object.


The nervous system allows the movemnt, but this is only possible if the brain transmits the command correctly.
to talk about the motor development we have to take into account the laws of growth and physical development. The motor development is produced by:
Cefalocaudal low: development occurs from the upper body (the head), to the bottom ( feet).
Proximodistal law : is produced from the central part towards the extremes of the body. The child controls before the movements of the arms than the hands,and the movement of the hands prior to the fingers.
Flexors and extensors law: The flexors are the muscles that flex the joints and the extensors are the muscles that provoque the aperture of the joints. The child lean first to pick up an object than drop out the object.

The nervous system allows the movemnt, but this is only possible if the brain transmits the command correctly.